√ Armored plates, kevlar, armored bags






1. Basic concepts
2. Ballistic materials
3. Protection classes
4. Protection of the VVO and arteries
5. Balance between protection and mobility
6. Types of injuries
7. FAQ
Can a Human not feel the impact of a bullet through armor plates?
What armor plates will protect against edged weapons?
Can armor plates protect against fire?
Is it true that when a bullet hits closer to the edge of the armor plate, its protective function decreases?
Is there an expiration date for armor plates?
What armor plates lose their properties when wet?
8. Where to buy armor plates
1. Basic concepts and terms related to body armor
Bronestal is a high-alloy hardened steel, the plates of which I use as protective plates for bulletproof vests. Protects against almost any small arms caliber up to 7.62 inclusive, can withstand a dozen shots, relatively low price. Of the disadvantages of steel armor plates - significant weight.
Kevlar is an aramid fiber woven into a very strong synthetic fabric in a special way; when wet, Kevlar loses its strength and some of its protective properties. It protects well against blunt bullets from pistol cartridges, but is easily penetrated by pointed bullets from automatic weapons.
Polyethylene is a high molecular weight polyethylene, many sheets of which are soldered under high pressure by manufacturers into a bulletproof plate. Ballistic impact resistance of polyethylene is 25% higher than that of Kevlar.
Ceramics is an inorganic material (usually silicon carbide or aluminum oxide) that is quite light, with maximum strength - a minimum level of behind-the-line injury. Among the disadvantages: it is destroyed from one shot, high price, the use of ceramics is advisable only for armor of high protection classes.
The armor package is an armor plate with a damper. Improved armor packages have an anti-ricochet layer made of reinforced rubber, Kevlar or aluminum.
Cover - a cover is actually a fabric vest (unloading system), in special pockets of which armor plates are placed.
Damper - a shock-absorbing layer in an armored package that provides additional protection.
Obstructive injury (armor injury) - contusion or blunt trauma to internal organs from the impulse that the bullet transmits to the armored plate, and the plate, in turn, to the human body. In light bulletproof vests, it is the damping of the contusion impact on a person that is especially important, and this task is not an easy one, it is much easier to ensure the impenetrability of the borne plate than to protect a person from multiple fractures, internal injuries and bleeding.
Armor-piercing bullet - a special projectile designed to destroy lightly armored targets. Armor-piercing ability is achieved through the use of superhard alloys in the core or in the bullet body itself.
Neck protection - modern armor protection designs provide additional elements, in particular to protect the neck and arteries - these are large and small collars made of soft (Kevlar) armor panels, these also include the much-needed groin protection (due to the location of vital arteries).
2. Ballistic materials of armor plates: Kevlar, polyethylene, ceramics and metal
In the manufacture of protective plates for bulletproof vests, various ballistic materials are used. The main ones are Kevlar, polyethylene, ceramics and metal. And the way to check the quality of armor plates is a shot. The most common slab shapes are rectangle, rounded rectangle and irregular hexagon. In addition, armor plates are flat and anatomically shaped.
2.1. How Kevlar Armor Plates Work
When a bullet hits a Kevlar armor plate , it penetrates "a web" of very dense fibers. They absorb and dissipate the impact energy that is transferred to the vest from the bullet, which deforms and flattens in the process.
Additional energy is absorbed successively by each layer of material until the bullet is stopped.
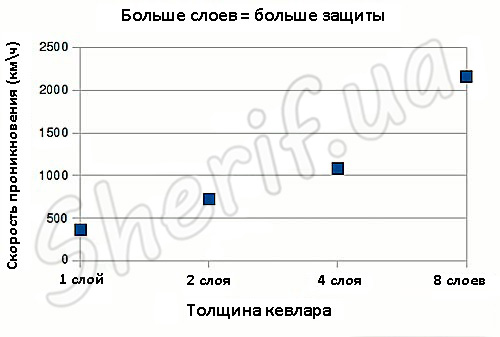
Since the fibers work both together and in each individual layer, this helps to prevent so-called blunt trauma to the internal organs. Currently, there is no such material to make the bulletproof vest single layer. The more layers, the stronger the Kevlar package, the higher the speed of the fired bullet must be to pierce it. Due to its flexibility and low weight, Kevlar is indispensable for protecting the neck and groin.
Kevlar resists well soft lead bullets, as well as blunt (rounded) jacketed bullets, for example, from PM.
Kevlar almost does not hold sharp-pointed steel-core bullets, for example, 7.62x39 LPS or 5.45PP. Such bullets have high kinetic energy, and the pointed shape simply pushes the fibers apart, the effectiveness of the armor is drastically reduced. It is impossible to attribute Kevlar to serious protection against edged weapons. It is not so easy to cut it with a knife, but it is very easy to pierce it with something sharp, for example, with an awl, like pointed rifle bullets, it simply pushes the fibers apart. Due to the layering, Kevlar can protect against blade-type combat knives.
Kevlar properties:
- Very durable, plastic, light weight material. Kevlar has a high tensile strength (eight times that of steel wire).
- Unlike most synthetic fabrics, Kevlar is difficult to melt. This material resists high temperatures quite well and only decomposes at about 450°C.
- Low temperatures have no effect on Kevlar. When tested by DuPont, neither brittleness nor material degradation was found (down to -196°C).
- Unlike a related material called Nomex, Kevlar can ignite, but will stop burning when the source of fire is removed.
- As with other plastics, prolonged exposure to ultraviolet light, such as sunlight, will cause discoloration and somewhat degrade Kevlar fibers.
- Another drawback is that Kevlar largely loses its properties from moisture, it easily absorbs water.
- Kevlar can withstand a variety of chemicals, although exposure to strong acids or alkalis will break it down over time.
2.2. How polyethylene armor plates work
Polyethylene is often confused with Kevlar, but it is a completely different material. Polyethylene is a special ultra-high density ballistic material. In English, such polyethylene is called "high-modulus or high-performance polyethylene" (abbreviation - HM PE or HP PE).
Polyethylene armor panels are simple in design, but difficult to manufacture. They consist of a large number of layers of polyethylene fibers and films, which are pressed into a single whole using high pressure.
Polyethylene has high strength, it is used to produce rigid armored panels of class III (according to the US system) and classes 2-3 according to the Ukrainian standard (DSTU B 4104). At the same time, polyethylene armor panels will protect against any kind of edged weapons. Since polyethylene is afraid of fire, B-32 armor-piercing incendiary cartridges with a special thermal composition are dangerous for polyethylene armor plates - when they hit an obstacle or target, such bullets form a lot of sparks.
Polyethylene properties:
- High molecular weight polyethylene is a thermoplastic substance with a low melting point (140-150°C).
- Polyethylene is frost-resistant, but is afraid of temperatures above 80-100°C.
- Water does not change the properties of polyethylene, it repels moisture (for example, the strength of wet Kevlar becomes 2 times less, and does not fully recover when dried).
- PE is not affected by acids, it is not afraid of ultraviolet radiation and microorganisms.
- Under conditions of long-term static load, polyethylene can stretch (“creep”).
- The tensile strength of polyethylene is 10 times higher than that of steel, and approximately 35% greater than that of Kevlar and similar fabrics.
- Ballistic impact resistance of polyethylene is 25% higher than that of Kevlar boards. Kevlar is almost twice as heavy as polyethylene.
2.3. How ceramic armor plates work
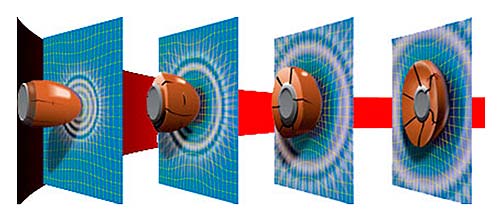
Ceramics is a non-metallic, inorganic, composite material of a complex, multicomponent structure. Ballistic ceramic plates are typically made up of silicon carbide or aluminum oxide. However, it makes no sense to use exclusively ceramics - this material is quite fragile. That is why composite ceramic armor packages have become widespread, they are reinforced with reinforcing materials similar to Kevlar. Typically, the armor package is a composite panel of a layer of ceramic (from the side of the bullet) and a layer of Kevlar (from the side of the body), and so on several times. An example of a Grade 6 multi-layered ceramic plate .
On impact, most of the kinetic energy is absorbed by the tough ceramic plate , which crumbles to powder at the point of impact. The residual energy of the bullet, the bullet itself and the ceramic fragments that continue to move, are absorbed by the reinforcing substrate (the choice of substrate material is determined by the structural requirements of ballistics and optimal weight). The purpose of the ceramic armor plate is to absorb most of the bullet's energy and distribute the remaining energy to the armor underneath the ceramic.
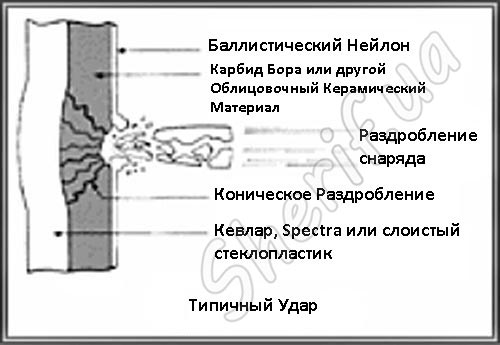
 The figure schematically depicts the process of a bullet hitting a SAPI (Small Arms Protective Insert) panel - a ceramic composite panel with a reinforcing substrate, they are used by the US military.
The figure schematically depicts the process of a bullet hitting a SAPI (Small Arms Protective Insert) panel - a ceramic composite panel with a reinforcing substrate, they are used by the US military.
As a rule, bulletproof ceramic panels are multi-layered, the figure below shows what such a panel is composed of. The top layer is ballistic nylon (a layer of loosely woven aramid fabric that is supposed to slow down the bullet speed), the middle or second layer is the ceramic itself - silicon carbide or another possible composition. And the very last, third layer is either several layers of Kevlar or a fiberglass laminate. In addition to the fact that these layers are designed to reduce the speed of the bullet, they flatten it so that the bullet does not penetrate the last layer, each of the layers has its own task.
Ceramic properties:
-
 Ceramics have very high ballistic resistance.
Ceramics have very high ballistic resistance. - However, ceramic protection does not work well at dissipating kinetic energy, resulting in blunt trauma more often.
- Ceramics are reinforced with other materials such as aramid fabrics, HDPE or metal.
- The ceramic plate, when hit by even the weakest bullet, is actually destroyed in an area of about 5 cm.
2.4. Metal armor plates
The Sheriff website presents protective plates made of armored steel from the European manufacturer Ruukki. This company has over 50 years of experience and all steel is made in Northern Finland.
Armored hot-rolled Ramor 500 steel is excellent protection against bullet and shrapnel wounds. The number in the name of the steel indicates its medium hardness (HBW). With proper processing, bending and cutting, Ramor armor steel retains ballistic properties along the edge of the plate.
For some types of imported vests, only beveled plate shapes are suitable. A simple rectangle will simply not fit in many imported vests. Cut edges are needed in order not to interfere with the movement of the fighter.
There are also side panels in the catalog of the Sheriff online store , most often they use side plates of the 2nd class , the 4th class is installed quite rarely. However, they are on sale. Doubts about the advisability of using the 4th class on the sides are due to the fact that the strengthening of the protective properties leads to a decrease in the mobility of the fighter (weight increases).
When a 7.62x39 bullet hits a class 4 side plate, there is a chance of serious damage to internal organs, even traumatic shock (when hit at a right angle). Our side plates are equipped with all sorts of additional layers, such as shock-absorbing damper, after which they are tested on the test site. The decision to buy such a plate is tantamount to choosing between the penetration of a bullet into the tissues of the organs or a strong blow to these very organs, so it is up to you.
Sheriff cuts protective armor plates from standard factory metal sheets (2, 3, 4 protection classes). After cutting, the edges are processed and sent to the paint shop, where the armored steel is powder coated by baking in an oven. Such painting, subject to the technology, will last a long time and save the armor from corrosion.
Under the order we can make any size. The site presents only typical (standard) sizes for the vests available in the catalog, as well as enlarged plates 29.5x37 cm. They do not fit in every case, so it is better to get advice from the seller or another specialist. For example, the following models of unloading vests are suitable for oversized armor plates: "Dnepr-2" KHAKI , WDL-MAX .
 Steel of the Ramor 500 brand is almost indestructible from shots from any type of automatic weapon; when fired from a Dragunov rifle (cartridge bullet 7.62x54), frivolous marks remain on the surface of the armor plate .
Steel of the Ramor 500 brand is almost indestructible from shots from any type of automatic weapon; when fired from a Dragunov rifle (cartridge bullet 7.62x54), frivolous marks remain on the surface of the armor plate .
The chipping from the 7N10 cartridge from the AK-74 does not exceed 2 mm, there is almost no space behind the barrier (DSTU allows up to 2.5 cm). In order to prevent blunt injuries, there is a cushioning layer. As a damper for Sheriff armor plates, either light porous rubber or isolon material up to 20 mm thick is used, depending on the model of the vest, since plates with a thick damper layer simply do not fit into some vests.
Metal armor plates withstand several dozen shots without destruction, unlike ceramic ones. The only requirement is that the impact points of the bullets are more than 1 cm apart.
In some tests, when hit from the SVD with two LPS bullets, the plate withstood even with a distance between shots of 5 mm. At the same time, the space behind the barrier slightly increased, from 2 mm to 4 mm.
3. Protection classes of armored plates and types of ammunition
The protection class of the armor plate and its durability depend on many factors: the weapon being fired from, the type of bullet (normal, steel-core, armor-piercing, tracer), bullet speed, distance to the shooter (point-blank or from afar), thickness and properties of the protective armor package.
The NIJ classification system (USA) has become widespread in the world. Classes are I through IV with II-A and III-A in between, ranging from low-velocity pistol rounds to armor-piercing Winchester Magnum rifle cartridges. The American NIJ classification is more stringent, and only two protection classes, III and IV, can be considered suitable for the military. The fourth American class protects against all the most common modern bullets.
On the territory of Ukraine, standards for protection against small arms are specified in DSTU B 4104.
Briefly, this standard can be formulated as follows:
The 1st class of armor plates is the weakest and can only withstand a regular bullet from a Makarov pistol.
2nd class - added TT pistol, standard cartridge 7.62x25 mm with a steel core.
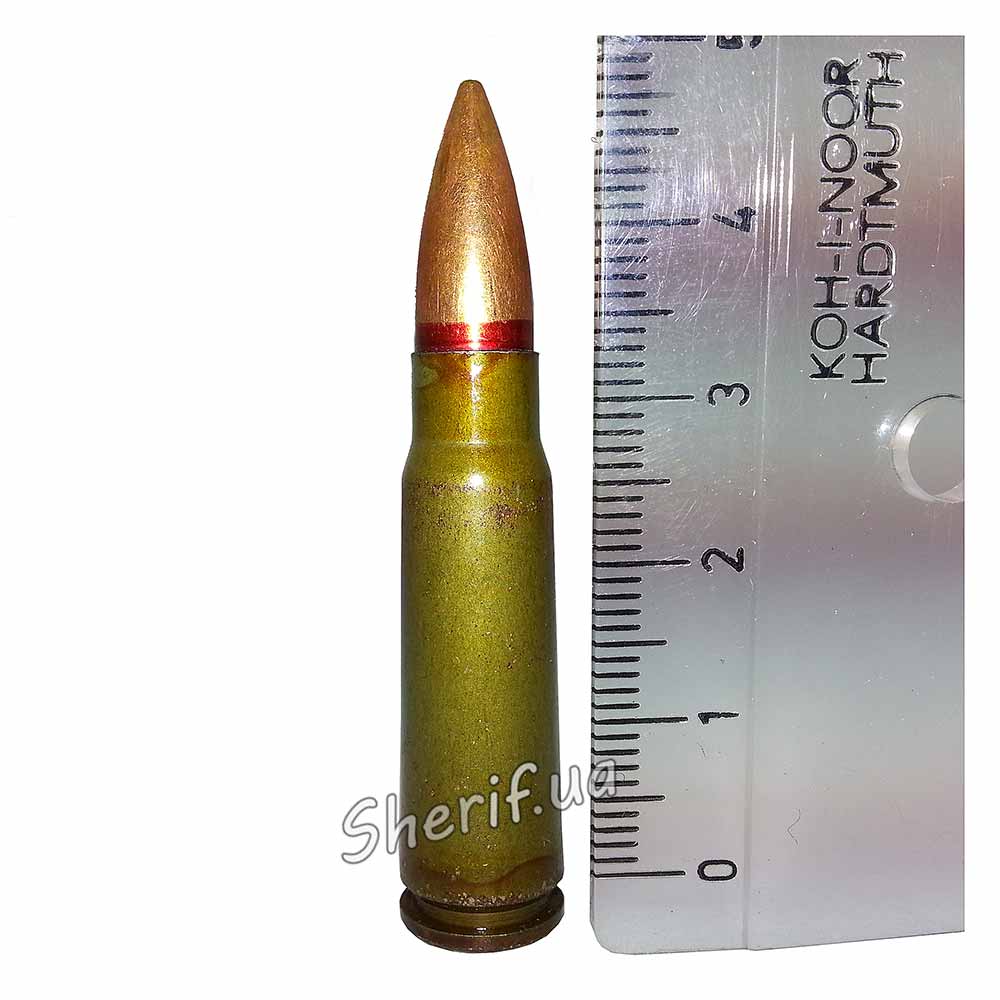 3rd class - plates of the third class hold only pistol cartridges and a regular AK-74 bullet (7.62X39 LPS with a red border).
3rd class - plates of the third class hold only pistol cartridges and a regular AK-74 bullet (7.62X39 LPS with a red border).
The 4th class must hold a bullet 7N10 (PP) 5.45x39 (AK-74), 7.62x39 LPS (AK, AKM, SKS).
Also, class 4 holds a lightweight bullet 57-N-223 with a caliber of 7.62x54 for SVD, it is also used in many types of machine guns.

Bullet for AK-74 5.45x39 PP, aka 5.45x39 7N10, with heat-strengthened core. This bullet pierces not so much due to kinetic energy, but due to the hardness of the core. Such bullets literally tear out pieces of metal. At the same time, the dent remains not very large, unlike 7.62 x 54 PS. The bullets of these cartridges also penetrate the 4th class according to GOST. Also, domestic class 4 does not guarantee protection against armor-piercing bullets of automatic weapons and the same SVD bullets.
5th class - protection stipulated by the 4th class plus protection against ammunition 7.62x54 with a heat-strengthened (armor-piercing) core without an incendiary composition (SVD weapons).
The latest class - 6A - is the highest degree of protection. Such armor plates can also withstand the armor-piercing incendiary cartridge 7.62x54 B32 under the SVD or analogues.
In combat conditions, it becomes necessary to defend against AK bullets and sniper rifles, from special armor-piercing and incendiary bullets. Soft armor is not suitable in such cases, hard armor or combined protection is needed here. 
In "Sheriff" you can buy the so-called armor packages - these are folded armor plates with a damper. In double armored packages, armor of the 3rd class of protection and an outer plate of the 2nd class were used. Between the plates is a shock-absorbing layer.
The first plate flattens the bullet, due to this deformation, it cannot penetrate the second layer. So it is possible to fight even with armor-piercing incendiary cartridges. The incendiary composition works when it hits the first plate and cannot burn through the 2nd. Such "sandwiches" are as effective as ceramic armor. They weigh more than ceramics, but their price is 2-3 times lower . The specificity of "sandwich" armor packages is that they can be restored and fully restored protective properties. A bullet hits the 2nd class plate, its remains remain in the damper layer, and the 3rd class armor plate remains intact. Such a kit has excellent anti-ricochet properties.
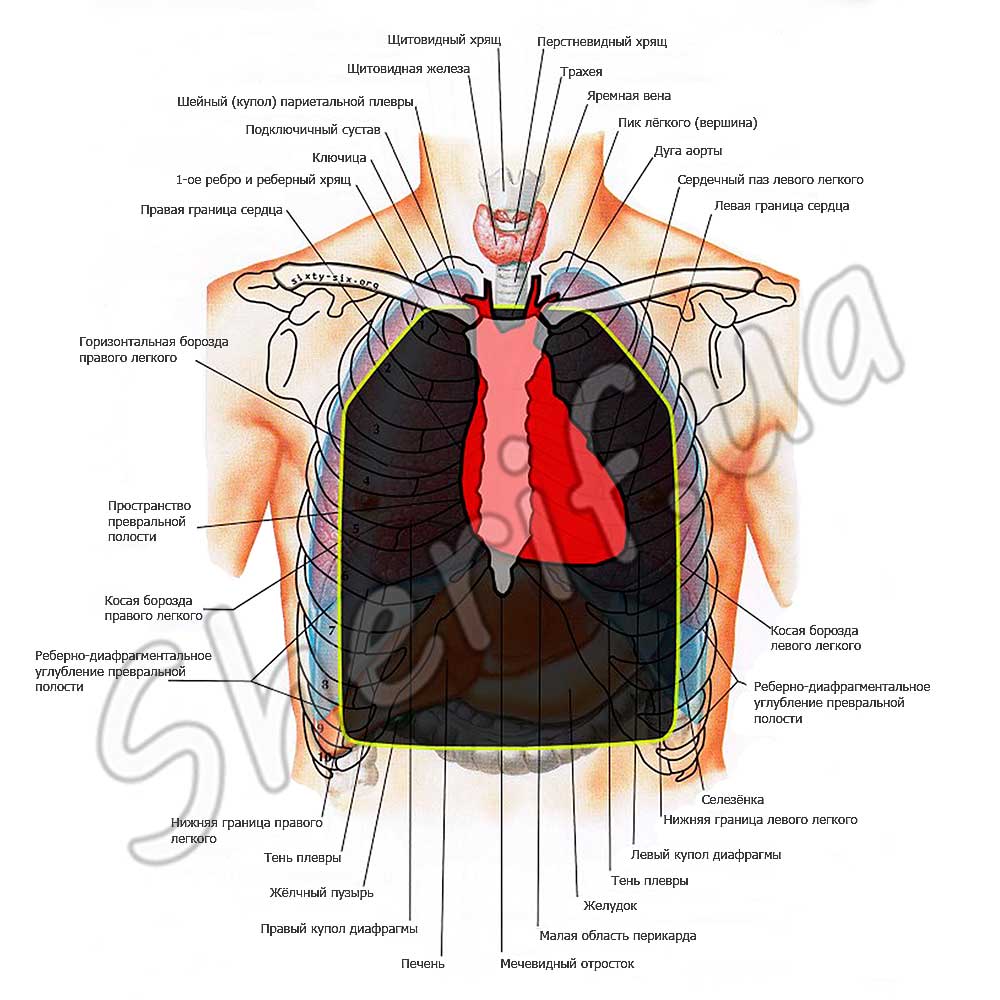
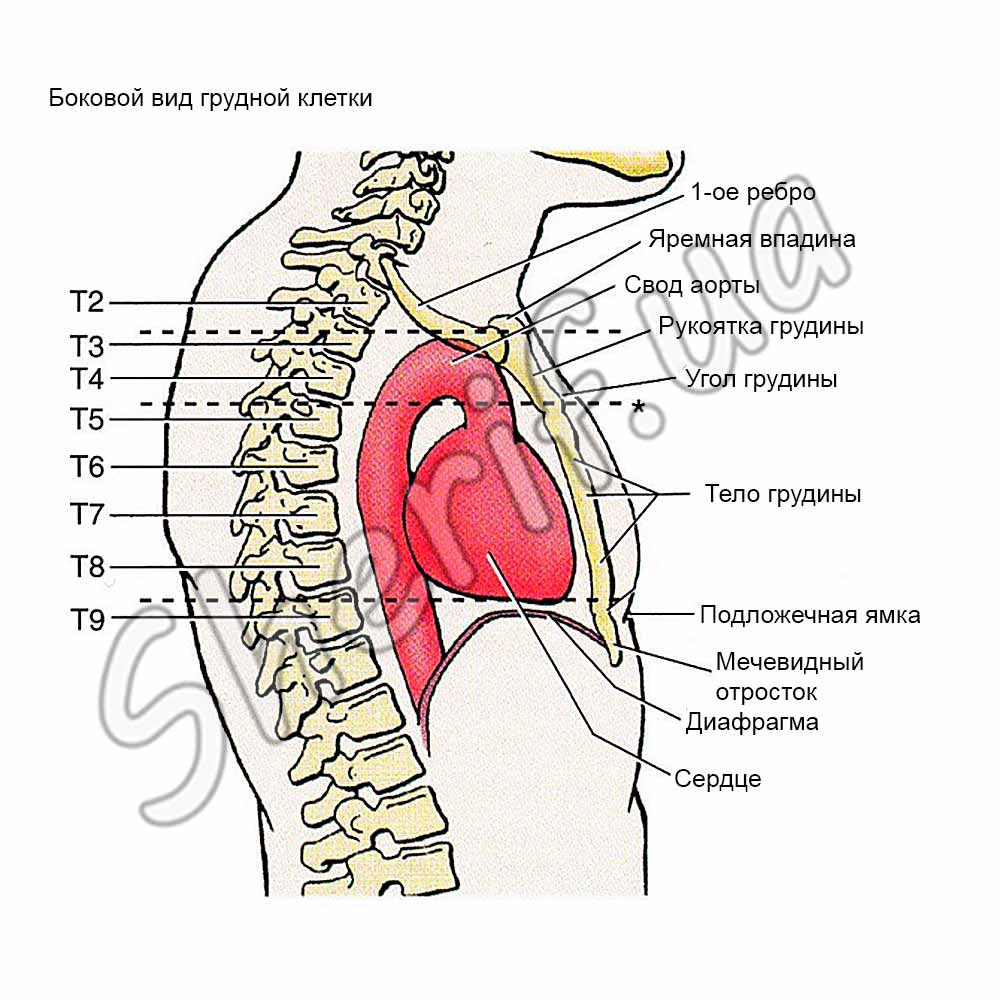
4. Protection of vital organs and arteries with armored plates
The main purpose of the armor plates is to protect the LHVO and large blood vessels, while a high degree of mobility is very important in combat.
The heart in the human body is located on the left, and its top is located approximately near the left nipple of the chest. The body armor plate must be chosen so that it covers the nipples to provide full protection of the heart. It should be noted that in some people the nipples may be slightly higher than the lateral apex of the heart.
The main blood vessels deliver blood to the heart and divert it - these are vena cava, pulmonary veins, aorta, pulmonary arteries. It is known that a blow to one artery can cause perforation of another and lead to massive hemorrhage. The most important of the three large vessels is the aorta, due to its size and high blood flow (about 5 liters per minute). A person with an average weight of 70 kg has about 5 liters of blood in the body. Thus, a wound in the aorta can bleed a person in one minute.
No less important is the diaphragm, its injury leads to impaired respiratory function. It is impossible to protect the diaphragm completely, but if the armor plates are installed correctly, it is possible to cover most of it. At this time, unfortunately, there is no complete protection of the spine. As for the lungs, death due to lung injury is possible due to pneumothorax and blood loss, but there is a better chance of salvation. It is almost impossible to gain time when injured in large arteries. The vessels of the liver and kidneys are not so easily damaged, therefore their protection is considered secondary.
5. Balance between protection and mobility with the location of armor plates
Plates must be sized. A properly installed plate should not cover the deltoid muscles, excess pressure on the shoulder quickly causes fatigue and discomfort. In some cases, plates that are too large can prevent a fighter from controlling small arms.
Plates that are smaller than required may pose a risk of injury to peripheral lung tissue and abdominal organs, but these organs can take a hit without lethal consequences.
5.1. Location of the front armor plate
The top of the plate should be at a level above the jugular notch. It should also line up with the top of the backplate when standing. An easy way to level the plates is to place your finger in the jugular notch with the top of the plate aligned with the bottom of the finger.
5.2. The location of the dorsal armor plate
Feel for the very last protruding bone of the cervical vertebrae (well-developed 6th cervical vertebrae). This tubercle is called the carotid tubercle; the common carotid artery or intervertebral disc adjoins it. Count two vertebral bones down or approximately 4 cm - this will be the upper point of the plate. As a result, the top of the back panel should match the top line of the chest plate.
5.3. Side and shoulder protection with armor plates
The side plates should protect the highly vascular elements of the abdomen. If the plates are placed high enough towards the armpits, the lower part of the heart can be protected. The shoulder plates have the same function - protecting the heart.
Correct position of the protective plates. The dark gray figure is a correctly positioned plate.
As a result:
• The front panel, even when standing, should cover the top of the sternum from nipple to nipple.
• Ideal when the back plate is one size larger than the front plate.
• The higher the side plates, the better.
6. Types of wounds and the use of armor plates:
 Shrapnel wounds do more harm and damage during combat than bullet wounds. This is warned by the existing publicly available statistics, which are based on the rates of gunshot and shrapnel wounds among those killed and wounded in different warring countries. Based on these statistics, the probability of death from a fragment is 3 times greater than from a bullet wound (data are given for hits in the limbs).
Shrapnel wounds do more harm and damage during combat than bullet wounds. This is warned by the existing publicly available statistics, which are based on the rates of gunshot and shrapnel wounds among those killed and wounded in different warring countries. Based on these statistics, the probability of death from a fragment is 3 times greater than from a bullet wound (data are given for hits in the limbs).
The movement of the fragments is called “tumbling”, the fragments almost immediately lose their speed due to the high resistance in the human body (unlike a bullet) and damage precisely the zone of their movement. There may be toxic substances on the surface of the fragments. The initial speed of a fragment can be 3000 m / s, and more such a fragment can inflict an open wound and kill. Fragments with a low speed of about 50 m / s cause closed injuries: bruises, damage to internal organs, serious fractures. Wound channels differ from fragments in their radial direction - from the center to the periphery. Shrapnel injuries are called complex because of the multiplicity and extensiveness of the lesion.
Also different are the damage from the impact of the so-called secondary projectiles - objects that were close to the epicenter of the explosion. It can be metal fragments and pieces of objects that are not visible to x-rays (glass, plastic, wood).

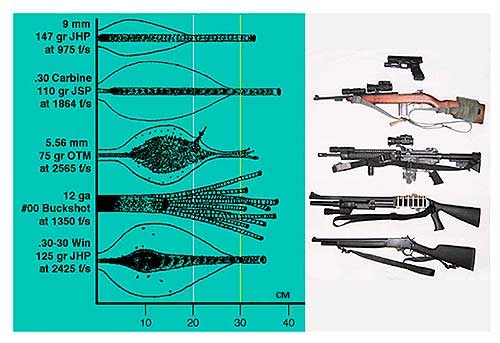
With regard to bullet wounds, the diagram above schematically depicts typical wound profiles (depending on bullet caliber) and the extent to which they have penetrated soft tissue. The steel core bullet demonstrates deep penetration with minimal tissue destruction relative to the vertical axis of the wound channel. The wound cavity reaches its largest size at the moment the bullet decelerates, when it begins to “tumble”. The figure shows that from high-speed tumbling bullets with a displaced center of gravity, the maximum dimensions of the cavity are formed at the very beginning of the wound channel, they easily ricochet and enter the body at an angle. This figure also shows wound profiles from a 9mm pistol, 30 round, and shotgun and rifle bullets.
At a long distance (from 500 meters and more) it is possible to protect yourself from an intermediate type bullet with the help of Kevlar. Bullets from a rifle and intermediate cartridges at close range are already a task for armor plates.
7. Frequently Asked Questions about Armor Plates:
Can a person not feel the impact of a bullet through armor plates?
Yes, it can, but only if weak bullets hit a hard armor plate. But a hit from an automatic weapon or a rifle can be felt even through hard armor.
In most cases of 5.45 and 7.62 bullet hits at a right angle, the fighter gets a fracture of the chest bones and severe hematomas that require long-term treatment.
What armor plates will protect from a knife or sharpening?
Serious protection against edged weapons can only be given by hard armored panels . Soft body armor can protect against blade-type melee weapons. Sharpeners, awls, and similar weapons with a double-edged blade will easily damage almost any number of layers of Kevlar.
Can armor plates protect against fire?
Depending on the material from which protective armor plates are made. So, aramid fiber does not support combustion, Kevlar is resistant to high temperatures. Soft armor panels can protect the body from burns if the cover for the armor plates is made of non-combustible fabric. As for polyethylene armor panels, which are often confused with Kevlar, they are just subject to combustion, their melting point is low - 80-100 degrees.
Is it true that when a bullet hits closer to the edge of the armor plate, its protective function decreases?
Soft armor does not protect as well when hit closer to the edge of the protective plate. Approximately at a distance of 5 cm from the edge of the panel, the armor resistance gradually decreases, with steel armor plates, with proper processing, this problem does not exist.
Is there an expiration date for armor plates?
Most manufacturers of Kevlar panels provide a 5-year warranty. Aramid twaron vests are guaranteed for 10 years. After the expiration date, it is better to change the armor, of course, the body armor will turn into a useless vest not one day after the warranty expires, but over time, the probability of holding a bullet, especially at the edges, will become higher and higher. Metal armor plates have an advantageous distinctive feature - they are not subject to the concept of "shelf life".
Which armor plates weaken the protective functions from moisture?
Kevlar loses up to 40% of its strength by absorbing moisture. As a rule, aramid fibers are protected by a cover made of a special waterproof fabric, or various impregnations are used that allow the bulletproof vest not to lose its protective properties even with prolonged and intense contact with water.
8. Where to buy body armor and armor plates
Prices for armor panels vary depending on the protection class, on their ballistic resistance and, of course, on the protective material. Voentorg Sheriff offers armor plates of different protection classes: 2nd, 3rd, 4th, 5th and 6th, all the main materials used in the production of armor plates are Kevlar and polyethylene, soft and hard, combined ceramic , as well as from Finnish armor steel and armored packages from a Ukrainian manufacturer. The sherif.ua online store will deliver your order to any city in the country. You can also buy armor plates and vests directly in Dnepropetrovsk at the address: st. Artem, 9.
(068) 798-0000 (063) 798-9999 (068) 300-5000
(068) 300-5000